Understanding Sewage Ejector Pumps
What is a Sewage Ejector Pump?
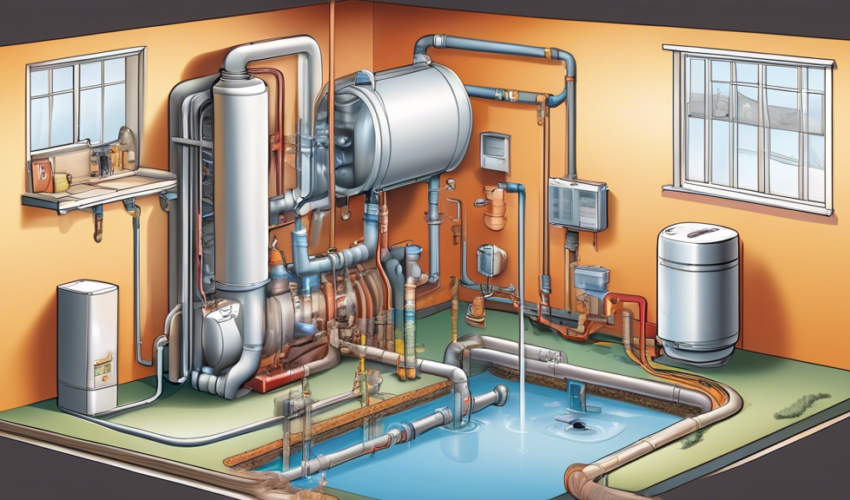
A sewage ejector pump is a vital system used in residential, commercial, and industrial plumbing to move sewage liquids and solids from one location to another, usually from lower to higher elevation. This type of pump is essential when bathroom fixtures are located below the main sewer line grade or in basement-level applications where gravity flow is impractical. The primary function of a sewage ejector pump is to handle waste material and transport it safely into the sewer system or septic tank, ensuring the proper functioning of a facility’s drainage system.
Key Components and How They Function
A typical sewage ejector pump system comprises several components, each crucial for its efficient operation. The main parts include:
- Pump: The pump itself is usually installed at the lowest point of the sewage basin. It is responsible for moving the effluent upwards towards the sewer line.
- Basin: A basin or sump pit is a holding container for waste water. The sewage from household fixtures flows into this basin.
- Float switch: This device triggers the pump to start when the sewage level rises to a pre-determined point and stops it after the level decreases.
- Check valve: The check valve prevents the backflow of sewage into the basin when the pump shuts off.
- Vent: Vents are essential for preventing gas build-up within the system and maintaining pressure balance which facilitates wastewater flow.
The pump operates on electricity and can be automatic or manual. Automatic pumps are equipped with sensors to detect the water level which activates the operation. Manual pumps, on the other hand, require physical activation to operate.
Installation Process of Sewage Ejector Pumps
Proper installation of a sewage ejector pump is crucial for functionality and longevity. Here’s a general process that professionals follow:
- Location and Preparation: Choose the location for the sewage pump, generally in the basement or lower level of the building where waste accumulates. Prepare the site ensuring it is clean and accessible.
- Installing the Basin: Dig a hole where the basin or pit will be installed. The size of the pit depends on the pump’s specifications generally provided by the manufacturer.
- Pump and Switch Installation: Place the pump inside the basin. Attach the float switch according to the manufacturer’s instructions to ensure it will trigger correctly at designated water levels.
- Plumbing connections: Connect the pump to the existing drainage system using PVC pipes. Ensure connections are tight to prevent leaks.
- Check Valve Installation: Install a check valve on the outlet pipe to prevent backflow of sewage.
- Venting and Power Supply: Properly vent the system to allow gas escape and connect the pump to the power supply. Ensure all electrical connections comply with local codes and safety standards.
- Testing: Before full use, test the pump and check all connections for leaks or errors in setup.
Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance is crucial to prolong the service life of a sewage ejector pump. Maintenance tips include:
- Routine checks for any clogs or blockages in the pit or inlet pipes.
- Inspecting the float switch and ensuring it runs freely without obstructions.
- Testing the pump periodically to ensure it operates and switches off as expected.
- Checking batteries if backup systems are installed, ensuring they are charged and functional.
By understanding and properly managing a sewage ejector pump, homeowners and property managers can effectively maintain their plumbing systems, preventing unpleasant sewage problems and potential damages.